Are you wondering what ACB and VCB is?
What are their major differences?
In this post, we will guide you about the modifications of these two.
What is VCB?
VCB refers to a vacuum circuit breaker.
It is a type of circuit breaker where the arc quenching takes place in the vacuum.
You see;
The technology is ideal for medium voltage application.
What about for higher voltage?
Vacuum technology has been designed but not viable commercially.

The operating of closing and opening of current carrying associate arc interruption and contacts happen in a vacuum chamber.
It’s located in the circuit breaker referred to as a vacuum interrupter.
This is composed of a steel arch chamber in the middle.
It is arranged symmetrically in ceramic insulators.
The vacuum pressure within a vacuum interrupter is typically sustained at 10-6 bar.
The material utilized for current carrying contacts plays a vital in the performance of VCB.
In fact, Cr/Cr is the perfect material to make vacuum circuit breaker contacts.
What’s more:
The vacuum circuit transforms to:
- axial magnetic field contact
- cut shape and;
- spiral shape
These days, VCB is considered as the most dependable current interruption technology for that medium voltage switchgear.
It needs less maintenance compared to other technologies of the circuit breaker.
How Does VCB Work?
When the contacts are separated because of abnormal conditions, the arc is struck in the contacts.
The arc is generated because of the ionization of metal oils.
This varies much on the material of the contacts.
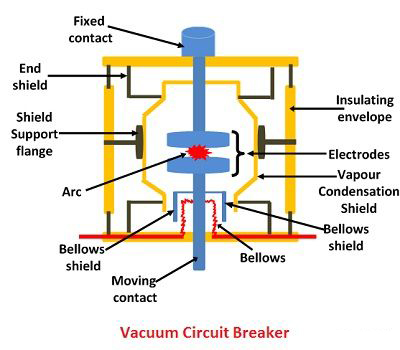
The arc interruption in the vacuum interrupters is different from other kinds of circuit breakers.
The separation of contact triggers the release of vapor.
You see;
That is filled in the contact shape.
It is composed of positive ions separated from the contact material.
The vapor density varies on the current within the arc.
If the current lowers, the rate vapor release lowers.
After current zero, the medium recovers its dielectric strength when the vapor density is lowered.
If the current to be interrupted is small in a vacuum, the arc has various parallel paths.
The overall current is separated into different parallel arcs.
That will repel one another and spread throughout the contact surface.
That’s referred to as a diffused arc that could be interrupted easily.
During high values of current, the arc gets intense in small regions. It causes fast vaporization of the contact surface.
Furthermore,
The interruption of the arc is probably when the arc remains in a diffused state.
When it’s eliminated quickly from the contact surface, the arc will be strike again.
Take note:
Arc extinction in VCB is highly affected by:
- the shape of the contacts
- the material of the contacts
- method of considering metal vapor
The path of the arc remained moving.
That’s because the temperature at any one point won’t be high.
https://youtu.be/-sAHYqcYjqw
After this, there’s an accumulation of dielectric strength that is peculiar of the vacuum breaker.
They are ideal for capacitor switching.
They will provide a re-strick performance.
You see:
The small current is disturbed before natural current zero.
That might cause chopping whose level varies on the material of contact.
Pros of Vacuum Circuit Breaker
The vacuum provides the greatest insulating strength.
Thus, it has extreme superior arc quenching properties than another medium.
- No exhaust of gas to the atmosphere
- VCB is almost free of maintenance
- Noiseless operation
- No fire hazard
- The explosion is prevented, enhancing the safety of the operating personnel
- VCB has a longer life
Cons of Vacuum Circuit Breaker
- The production of VCB is not economical when designed in small quantities
- The price of the breaker becomes too much at higher voltages.
That’s because high voltages more than 2 numbers of the circuit breaker are needed to be linked in series.
- The main drawback of VCB is that it is not economical, exceeding 38 kVolts.
What is ACB?
On the other hand:
ACB refers to an air circuit breaker.
It is an electrical device utilized to offer:
- short-circuit protection and
- overcurrent protection
for electrical circuits over 800 to 10K amps.
You can find these devices in distribution panels.

Take note:
ACB is a circuit operation breaker, which runs in the air as an arc extinguishing medium.
You will find different kinds of switching gears and ACB accessible in the market today.
Most of them are:
- high-performing
- durable
- simple to install and maintain
ACB has totally changed oil circuit breakers.
How Does ACB Work?
ACB work along with their contacts in the free air.
Their technique of arc quenching control is totally different from OCBs.
They are widely utilized for LV interruption.
Today, they are more likely to change high voltage oil breakers.
Generally, ACB has two pair of contacts:
- the arcing contact is made of carbon
- main pair of contacts made of copper metal
When the fault takes place, the main contacts are separated first.
The current is shifted to the arcing contacts.
You see:
The arcing contacts are separated, and the arc is drawn among them.
The arc is driven upwards by the:
- thermal action and;
- electromagnetic forces
The arc ends travel through the arc runner.
The arc shifts upward, and it is separated by the arc splitter plates.
The arc is extinguished by:
- splitting
- cooling
- lengthening and so on
Pros of Air Circuit Breaker
ACBs are utilized for controlling the:
- industrial plants and;
- power station auxiliaries
They provide protection to:
- industrial plants
- electrical machines such as generators, capacitors, and transformers
Other advantages of ACB are the following:
- ACB is utilized in the electricity sharing system as well as NGD at least 15kV
- ACB offers high resistance power, helping in raising the resistance of the arc by:
- lengthening
- cooling
- splitting
- The air brake principle of the ACB is utilized in AC circuits and DC circuits up to 12kV
Cons of Air Circuit Breaker
- The chute isn’t less efficient in its de-ionizing and lengthening action.
However, the arc action to the chute is more likely to become slower.
- It has inefficiency at low currents where electromagnetic fields are fragile.
In short, both VCB and ACB are the type of circuit breaker.
They are both utilized for the same purpose.
It is used for separating the supply unit and grip.
On the other hand;
ACB is commonly utilized for medium voltage use.
VCB is utilized for high voltage purposes.
